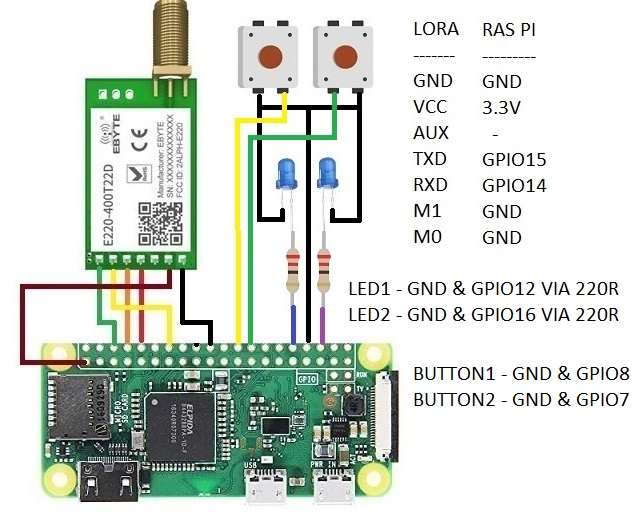
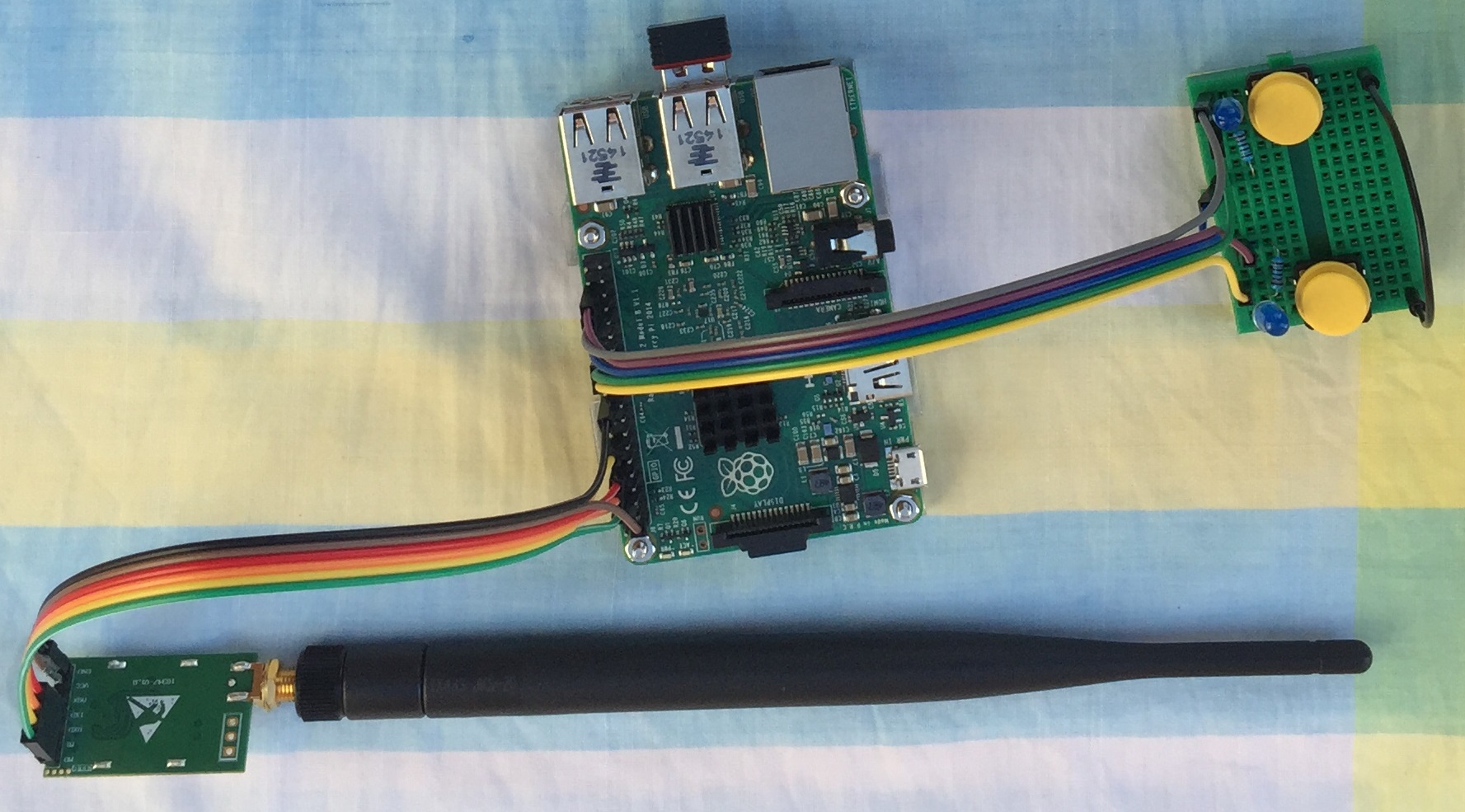
I have used two sets of Raspberry PI and Ebyte 433MHz UART LORA Module to transmit and receive data between long distance. This LORA module does not need library. We can simply use serial.write() and serial.read() to transmit and receive. When receiving we need to decode the data from character to integer. Manufacturer sets Channel, Address and key to default value so no need to change these until we complete basic circuit and do a distance testing. It will work out of the box. Make sure to use both modules with same part number. E220-400T22D module is rated for 5km distance. Because I used low voltage of 3.3V VCC, I was able to get about 500m (half km) easily without line of sight using about 25mW power.
Some countries uses different frequencies and power limitation for LORA transmission. After finding out these you can get the matching module from https://www.ebyte.com. Inexpensive items can be purchased from https://www.aliexpress.com/store/5489003. I bought my items from https://www.aliexpress.com/item/1005002091320352.html and the antenna from https://www.aliexpress.com/item/1005001530239330.html. For in-house testing we do not need the antenna. If we do not use antennas, we need to switch the power off for few minutes every hour to cool the module. The reason is RF power will be returned back to module if no antenna found and it will produce heat.
This project assumes you have already used Raspberry PI. You need to have completed a basic LED blink Program.
Open the terminal and type
sudo apt-get install python-serial
After completion, type
sudo raspi-config
Select Interface Options --> Select Serial Port
Would you like a login shell to be accessible over serial? NO
Would you like a login shell to be accessible over serial? YES
Click OK and then click Finish
Type
sudo nano lora.py
Copy and paste codes below
#Transmitter code starts here import time import serial import RPi.GPIO as GPIO GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BCM) GPIO.setwarnings(False) GPIO.setup(7, GPIO.IN, pull_up_down=GPIO.PUD_UP) GPIO.setup(8, GPIO.IN, pull_up_down=GPIO.PUD_UP) GPIO.setup(12, GPIO.OUT, initial=GPIO.LOW) GPIO.setup(16, GPIO.OUT, initial=GPIO.LOW) lora = serial.Serial('/dev/ttyAMA0', baudrate=9600, parity=serial.PARITY_NONE, stopbits=serial.STOPBITS_ONE, bytesize=serial.EIGHTBITS) time.sleep(1) relay1 = True relay2 = True #Detects button on/off and transmit to LORA def switch1(ev=None): global relay1 global relay2 relay1 = not relay1 if relay1 and relay2: lora.write("KEY3") elif relay1: lora.write("KEY2") elif relay2: lora.write("KEY1") else: lora.write("KEY0") def switch2(ev=None): global relay1 global relay2 relay2 = not relay2 if relay1 and relay2: lora.write("KEY3") elif relay1: lora.write("KEY2") elif relay2: lora.write("KEY1") else: lora.write("KEY0") GPIO.add_event_detect(7, GPIO.RISING, callback=switch1, bouncetime=300) GPIO.add_event_detect(8, GPIO.RISING, callback=switch2, bouncetime=300) try: while True: #Gets the feedback data and toglle LEDs if lora.inWaiting() > 0: data1 = lora.read() if data1 == 'Y' and lora.inWaiting() > 0: data2 = lora.read() if data2 == 'E' and lora.inWaiting() > 0: data3 = lora.read() if data3 == 'S' and lora.inWaiting() > 0: data4 = lora.read() if data4 == '0': GPIO.output(12, GPIO.HIGH) GPIO.output(16, GPIO.HIGH) elif data4 == '1': GPIO.output(12, GPIO.HIGH) GPIO.output(16, GPIO.LOW) elif data4 == '2': GPIO.output(12, GPIO.LOW) GPIO.output(16, GPIO.HIGH) elif data4 == '3': GPIO.output(12, GPIO.LOW) GPIO.output(16, GPIO.LOW) except KeyboardInterrupt: print "Exiting Program" except: print "Error, Exiting Program" finally: lora.close() pass #Transmitter code ends here
Type
sudo python lora.py
Open the terminal and type
sudo apt-get install python-serial
After completion, type
sudo raspi-config
Select Interface Options --> Select Serial Port
Would you like a login shell to be accessible over serial? NO
Would you like a login shell to be accessible over serial? YES
Click OK and then click Finish
Type
sudo nano lora.py
Copy and paste codes below
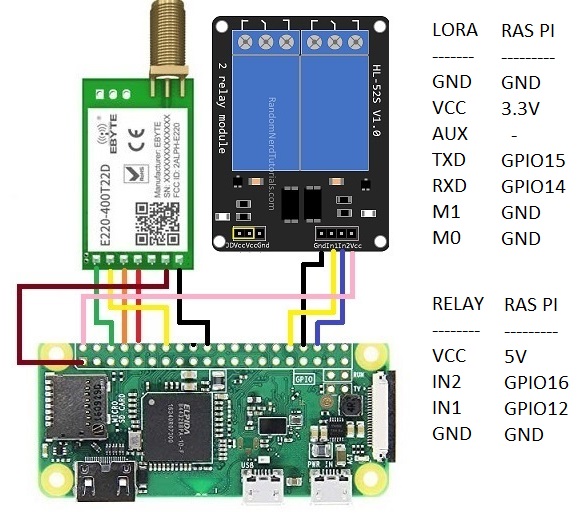
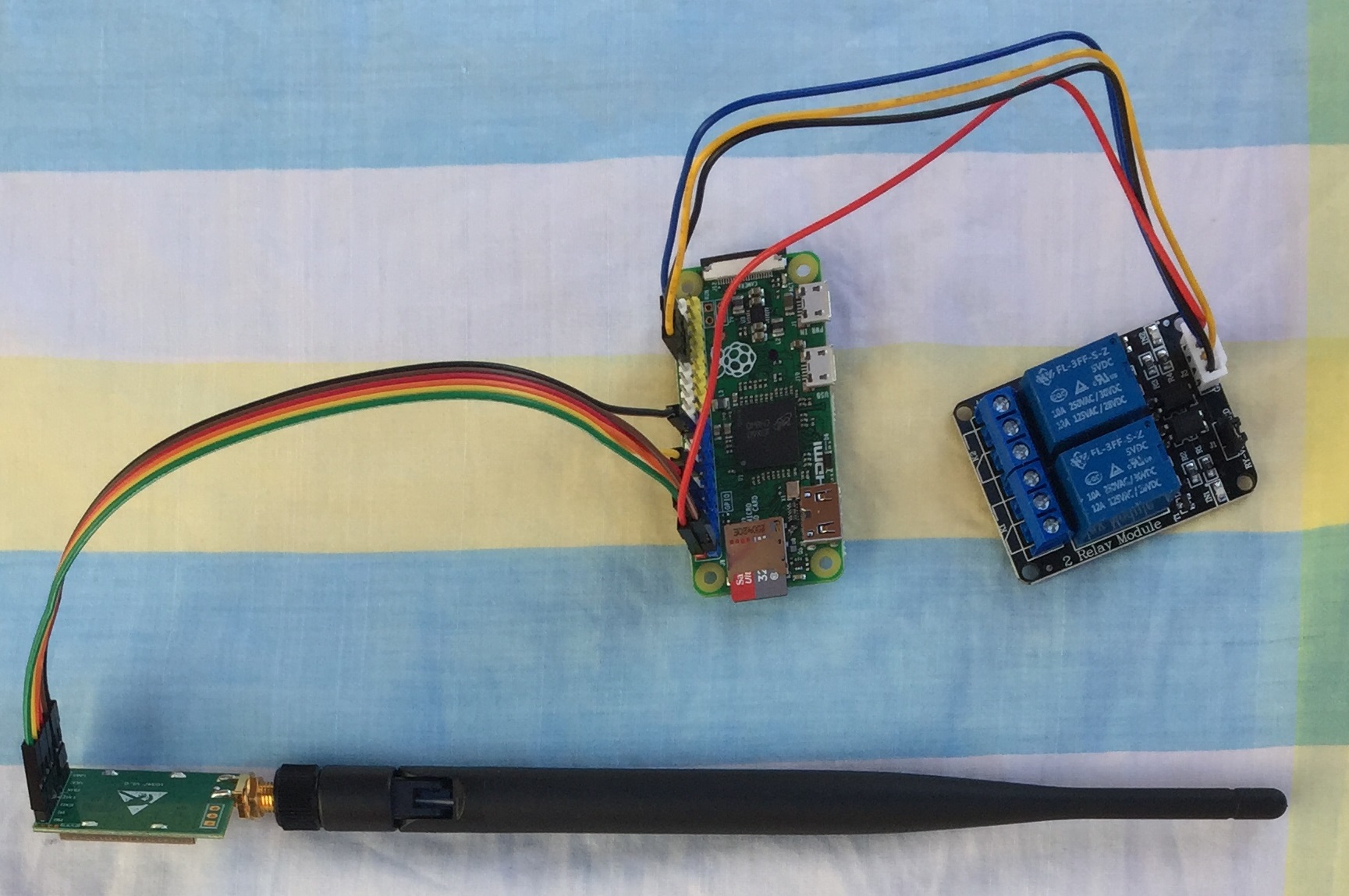
#Receiver code starts here import time import serial import RPi.GPIO as GPIO GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BCM) GPIO.setwarnings(False) GPIO.setup(12, GPIO.OUT, initial=GPIO.HIGH) GPIO.setup(16, GPIO.OUT, initial=GPIO.HIGH) lora = serial.Serial('/dev/ttyAMA0', baudrate=9600, parity=serial.PARITY_NONE, stopbits=serial.STOPBITS_ONE, bytesize=serial.EIGHTBITS) time.sleep(1) try: while True: if lora.inWaiting() > 0: data1 = lora.read() if data1 == 'K' and lora.inWaiting() > 0: data2 = lora.read() if data2 == 'E' and lora.inWaiting() > 0: data3 = lora.read() if data3 == 'Y' and lora.inWaiting() > 0: data4 = lora.read() if data4 == '0': GPIO.output(12, GPIO.LOW) GPIO.output(16, GPIO.LOW) lora.write("YES0") elif data4 == '1': GPIO.output(12, GPIO.HIGH) GPIO.output(16, GPIO.LOW) lora.write("YES1") elif data4 == '2': GPIO.output(12, GPIO.LOW) GPIO.output(16, GPIO.HIGH) lora.write("YES2") elif data4 == '3': GPIO.output(12, GPIO.HIGH) GPIO.output(16, GPIO.HIGH) lora.write("YES3") except KeyboardInterrupt: print "Exiting Program" except: print "Error, Exiting Program" finally: lora.close() pass #Receiver code ends here
Type
sudo python lora.py
If for some reason Raspberry PI restarts, the python script will not auto-launch. There is a instruction set on how to write a simple launcher script which can be found in https://www.instructables.com/Raspberry-Pi-Launch-Python-script-on-startup/
You can download RF-Setting software and manual from https://www.ebyte.com/en/data-download.html?id=579&pid=211#load. For this particular module Address range is 0~65535; Channel range is 0~83; Key rage is 0~65535. You can set combination of different Address and Keys to secure transmission. On top of it, you can use encrypted data and/or checksum bits as well.