Docs
Micro-controllers, wireless transmission and database
EEPROM AT24C Series with Blue Pill using STM32CubeIDE
Prerequisites
This project assumes you have already installed STM32CubeIDE. You need to have previously done a basic blink sketch with blue-pill using STM32CubeIDE. I have made a complete video from installing STM32CubeIDE to LED blink program. You can watch it by clicking this link. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kXg467nVd_A
Addressing
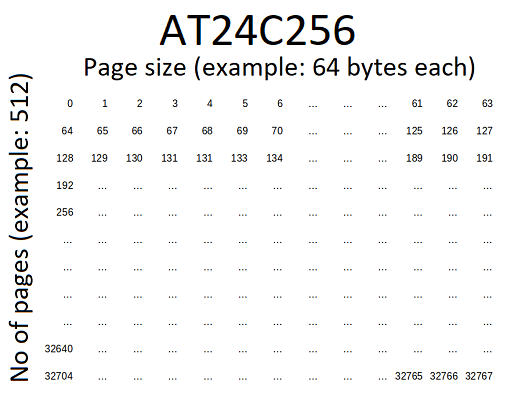
The module I am using is AT24C256. Datasheet is available at http://ww1.microchip.com/downloads/en/devicedoc/doc0670.pdf
AT24C256, 256K SERIAL EEPROM: Internally organized with 512 pages of 64 bytes each
Similarly,
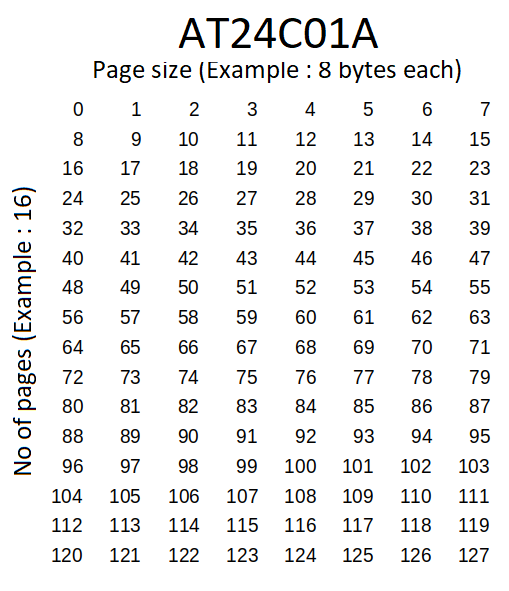
AT24C01A, 1K SERIAL EEPROM: Internally organized with 16 pages of 8 bytes each
AT24C02, 2K SERIAL EEPROM: Internally organized with 32 pages of 8 bytes each
AT24C04, 4K SERIAL EEPROM: Internally organized with 32 pages of 16 bytes each
AT24C08A, 8K SERIAL EEPROM: Internally organized with 64 pages of 16 bytes each
AT24C16A, 16K SERIAL EEPROM: Internally organized with 128 pages of 16 bytes each
And so on
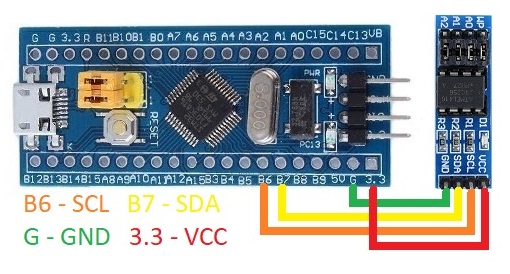
Wiring Diagram
STM32CubeIDE Settings
Click connectivity --> Click I2C1
For I2C select I2C
Configuration --> Parameter Settings
For I2C speed select Fast Mode
Additional code on top of STM32CubeIDE generated code
/* USER CODE BEGIN PV */ #define EEPROM_ADDR 0xA0 uint8_t toWrite1[] = "English is a WestGermanic language of the IndoEuropean language"; uint8_t toWrite2[] = "The STM32 family of 32-bit microcontrollers based on Arm Cortex"; uint8_t toWriteA[] = "Hello"; uint8_t toWriteB[] = "Hi"; uint8_t toWriteM[] = "Microcontroller is a compressed micro computer"; uint8_t toWriteL[] = "EEPROM stands for electrically erasable programmable readonly M"; uint8_t toRead1[64]; uint8_t toRead2[64]; uint8_t toReadA[5]; uint8_t toReadB[2]; uint8_t toReadM[64]; uint8_t toReadL[64]; /* USER CODE END PV */ /* USER CODE BEGIN 2 */ // HAL_I2C_Mem_Write(I2C_HandleTypeDef *hi2c, uint16_t DevAddress, uint16_t MemAddress, // uint16_t MemAddSize, uint8_t *pData, uint16_t Size, uint32_t Timeout); HAL_I2C_Mem_Write(&hi2c1, EEPROM_ADDR, 0, 2, toWrite1, sizeof(toWrite1), 1000); HAL_I2C_Mem_Write(&hi2c1, EEPROM_ADDR, 64, 2, toWrite2, sizeof(toWrite2), 1000); HAL_I2C_Mem_Write(&hi2c1, EEPROM_ADDR, 129, 2, toWriteA, sizeof(toWriteA), 1000); HAL_I2C_Mem_Write(&hi2c1, EEPROM_ADDR, 189, 2, toWriteB, sizeof(toWriteB), 1000); HAL_I2C_Mem_Write(&hi2c1, EEPROM_ADDR, 16000, 2, toWriteM, sizeof(toWriteM), 1000); HAL_I2C_Mem_Write(&hi2c1, EEPROM_ADDR, 32704, 2, toWriteL, sizeof(toWriteL), 1000); // HAL_I2C_Mem_Read(I2C_HandleTypeDef *hi2c, uint16_t DevAddress, uint16_t MemAddress, // uint16_t MemAddSize, uint8_t *pData, uint16_t Size, uint32_t Timeout); HAL_I2C_Mem_Read(&hi2c1, EEPROM_ADDR, 0, 2, toRead1, sizeof(toRead1), 1000); HAL_I2C_Mem_Read(&hi2c1, EEPROM_ADDR, 64, 2, toRead2, sizeof(toRead2), 1000); HAL_I2C_Mem_Read(&hi2c1, EEPROM_ADDR, 129, 2, toReadA, sizeof(toReadA), 1000); HAL_I2C_Mem_Read(&hi2c1, EEPROM_ADDR, 189, 2, toReadB, sizeof(toReadB), 1000); HAL_I2C_Mem_Read(&hi2c1, EEPROM_ADDR, 16000, 2, toReadM, sizeof(toReadM), 1000); HAL_I2C_Mem_Read(&hi2c1, EEPROM_ADDR, 32704, 2, toReadL, sizeof(toReadL), 1000); /* USER CODE END 2 */